
Plantar Surface of the Foot Diagram Quizlet
The foot is a complex structure comprised of over 26 bones, 30 joints, numerous tendons, ligaments, and muscles responsible for our ability to stand upright, supporting the weight of the entire body and provides the base for the mechanism for bipedal gait. The foot corresponds to the portion of the lower extremity distal to the ankle and divides into hind, mid and forefoot. The articular.

Anatomy of the Foot and Ankle OrthoPaedia
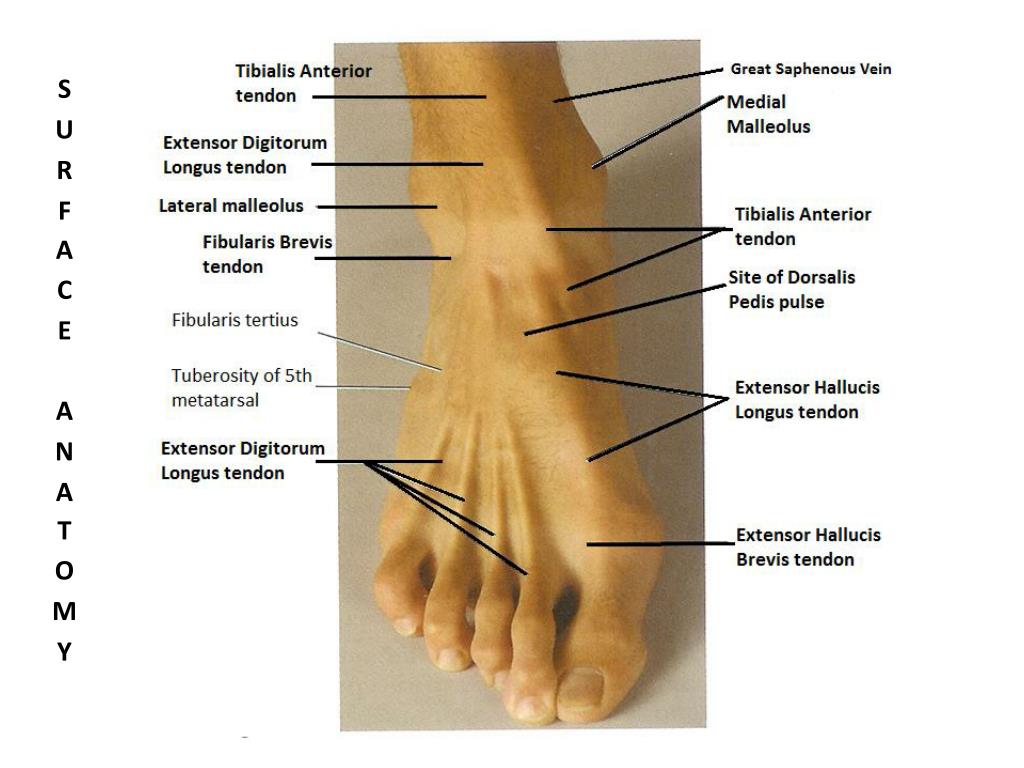
Surface Anatomy of the Foot Updated: May 27, 2023 In this section Cypress Foot and Ankle specialist Dr. Christopher Correa discusses Surface Anatomy of the foot ankle.

Muscles of the Plantar Surface of the Foot (1st layer) Diagram Quizlet
The largest bone of the foot, the calcaneus, forms what is commonly referred to as the heel. It slopes upward to meet the tarsal bones, which point downward along with the remaining bones of the.

Understanding the Foot and Ankle 1004 Anatomical Parts & Charts
Foot: Anatomy. The foot is the terminal portion of the lower limb, whose primary function is to bear weight and facilitate locomotion. The foot comprises 26 bones, including the tarsal bones, metatarsal bones, and phalanges. The bones of the foot form longitudinal and transverse arches and are supported by various muscles, ligaments, and.

Ankle Anatomy Sport Med School
The upper ankle joint is formed by the inferior surfaces of tibia and fibula, and the superior surface of talus. The lower ankle joint is formed by the talus, calcaneus, and navicular bone. The joint is supported by a set of ankle ligaments: the medial collateral or deltoid ligament, and lateral collateral ligament.
PPT BONES OF THE FOOT & ANKLE PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1164845
Figure 1. Sections and Bones of the Foot A. Lateral (Left) B. Anterior (Right) Figure 2. Compartments of the Foot A. Cut Section through Mid-Foot Figure 3. First Layer of the Foot A. Plantar View of Right Foot Figure 4. Second Layer of the Foot A. Plantar View of Right Foot Figure 5. Third Layer of the Foot A. Plantar View of Right Foot Figure 6.
Surface Anatomy Of Foot
Anatomy The foot and ankle form a complex system which consists of 28 bones, 33 joints, 112 ligaments, controlled by 13 extrinsic and 21 intrinsic muscles. The foot is subdivided into the rearfoot, midfoot, and forefoot.

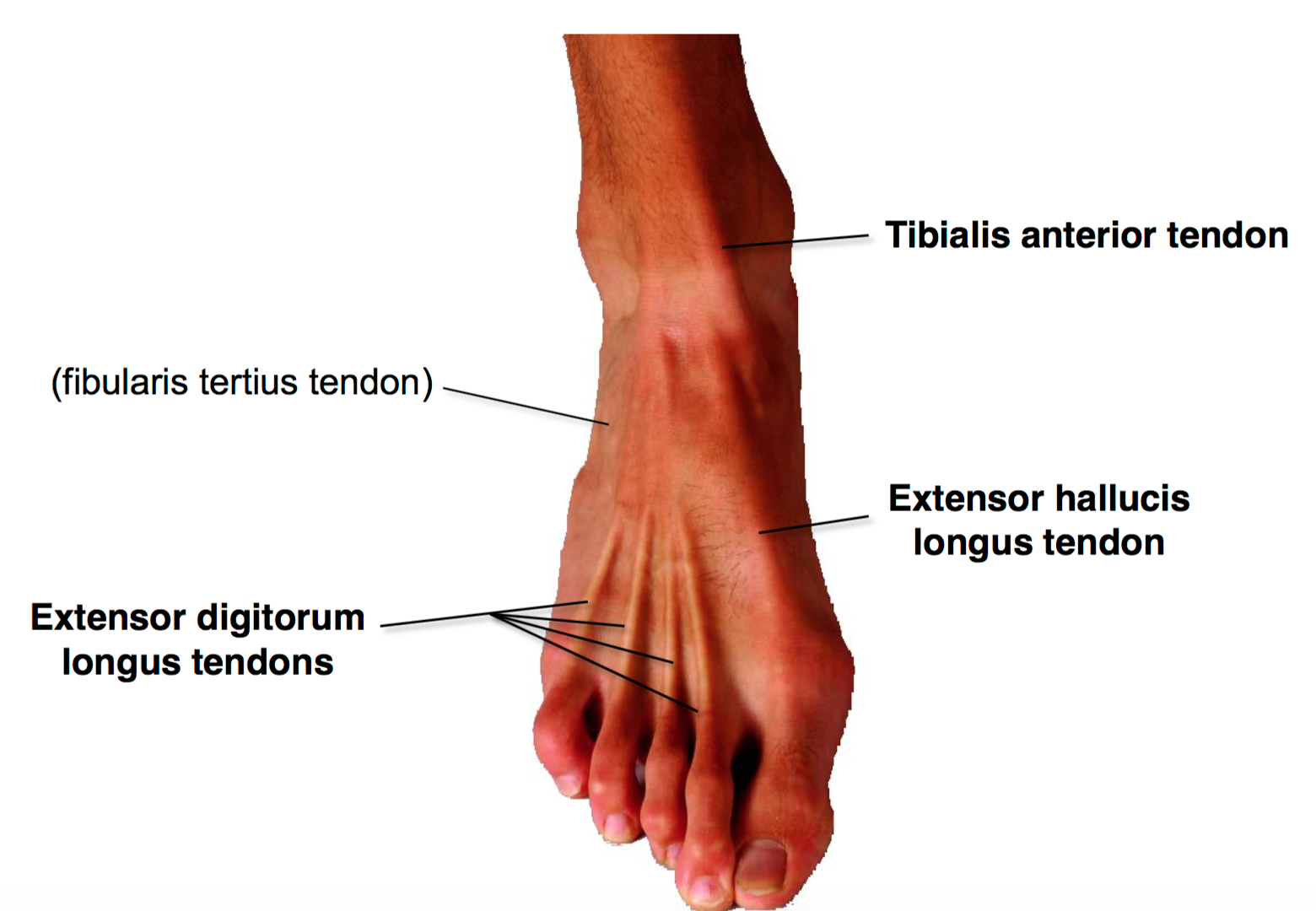
Dorsal Foot Art as Applied to Medicine
The foot is an intricate part of the body, consisting of 26 bones, 33 joints, 107 ligaments, and 19 muscles. Scientists group the bones of the foot into the phalanges, tarsal bones, and.

Body Types, Surface Landmarks, and SoftTissue Characteristics Classic Human Anatomy in Motion
Foot Anatomy and Biomechanics. base of the 5th metatarsal (lateral band), plantar plate and bases of the five proximal phalanges. plantar support is by the superficial and deep inferior calcaneocuboid ligaments. broad insertion over the lateral aspect of the lateral sesamoid and lateral aspect of the base of the proximal phalanx.

Anatomy of the Foot and Ankle (Plantar View) TrialExhibits Inc.
Last updated 2 Nov 2018 The anatomy of the foot The foot contains a lot of moving parts - 26 bones, 33 joints and over 100 ligaments. The foot is divided into three sections - the forefoot, the midfoot and the hindfoot. The forefoot

Foot Anatomy Plantar
Introduction A solid understanding of anatomy is essential to effectively diagnose and treat patients with foot and ankle problems. Anatomy is a road map. Most structures in the foot are fairly superficial and can be easily palpated. Anatomical structures (tendons, bones, joints, etc) tend to hurt exactly where they are injured or inflamed.
Foot Basicmedical Key
Anatomy of the Foot. The foot is one of the most complex parts of the body. It consists of 28 bones connected by many joints, muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The foot is prone to many types of injuries. Foot pain and problems can cause pain and inflammation, limiting movement. Muscles contract and relax to move the foot.

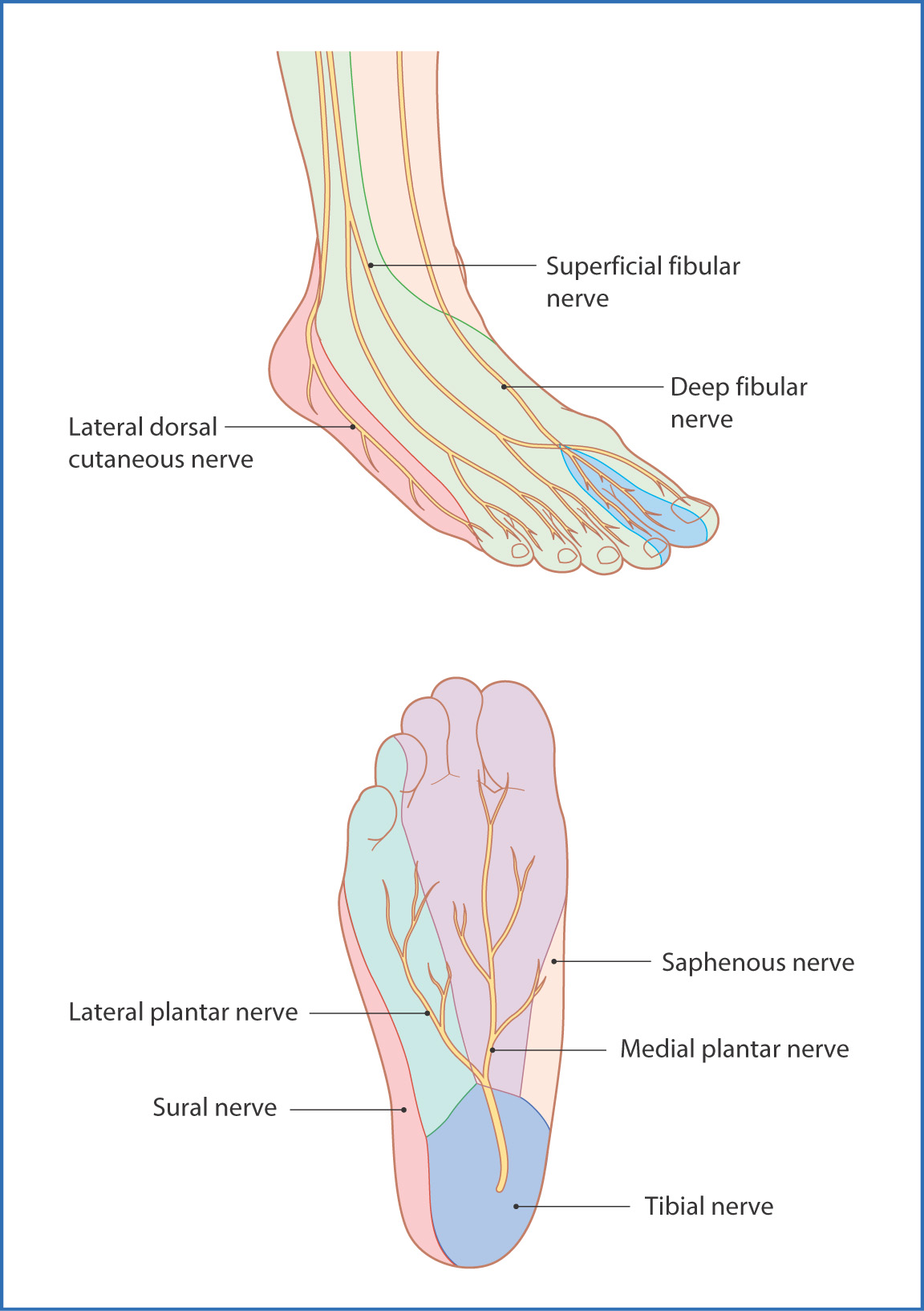
Atlas of Surface Anatomy Hadzic's Peripheral Nerve Blocks and Anatomy for UltrasoundGuided
What to know about foot anatomy Structure of the foot Conditions of the foot Summary The foot has a complicated anatomical structure with many parts, all of which have specific functions..
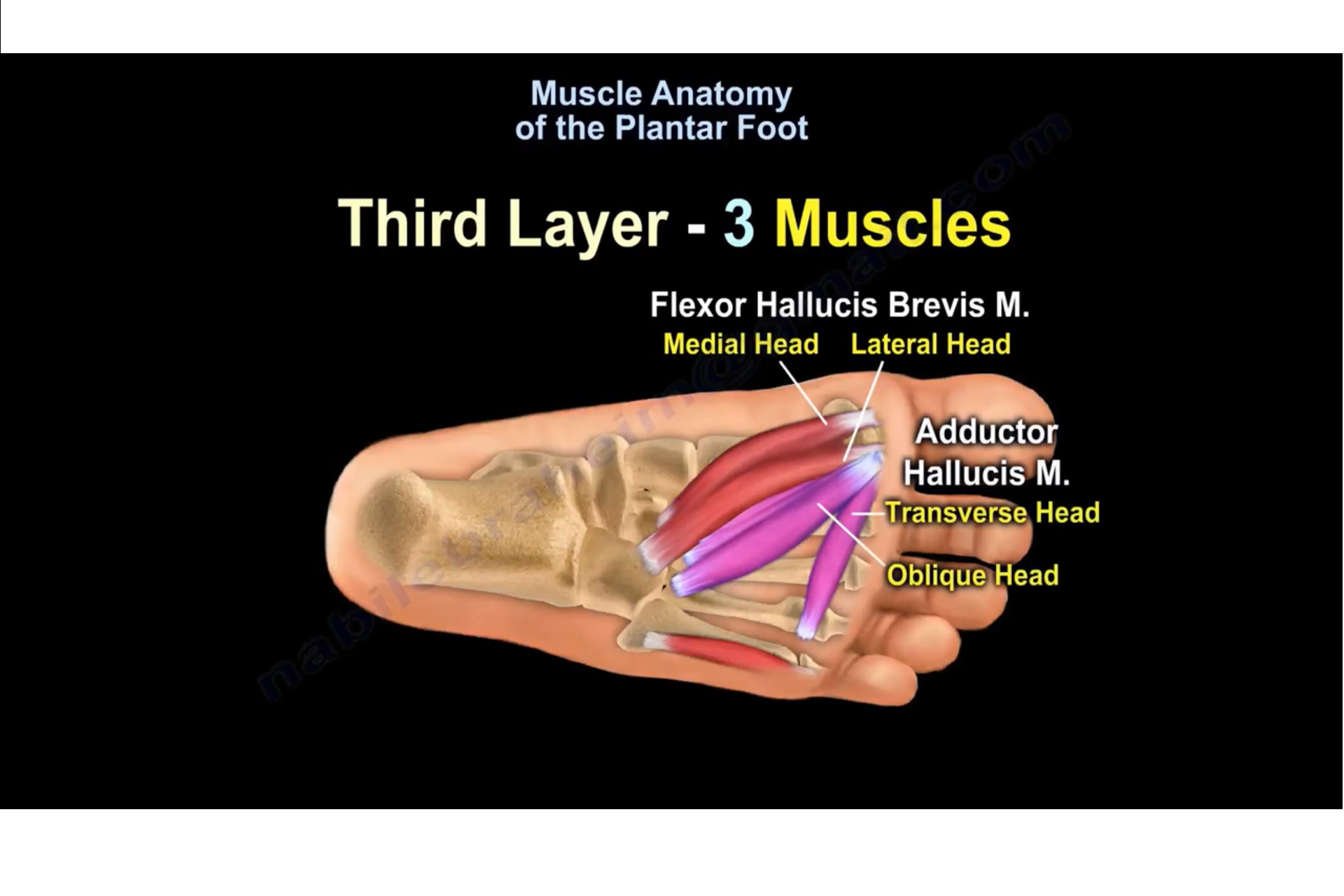
Muscle Anatomy Of The Plantar Foot —
The Foot. The foot is an incredibly complex mechanism. Each foot contains 26 bones, 33 joints, and more than a hundred muscles, tendons, and ligaments. These parts work harmoniously to get you from one place to the next. They do it all while handling hundreds of tons of force - your weight in motion - every single day.

Turf toe causes, signs, symptoms, recovery, diagnosis & turf toe treatment
The anatomic structures below the ankle joint comprise the foot, which includes: Hindfoot: The hindfoot is the most posterior aspect of the foot. It is composed of the talus and calcaneus, two of the seven tarsal bones. The talus and calcaneus articulation is referred to as the subtalar joint, which has three facets on each of the talus and.
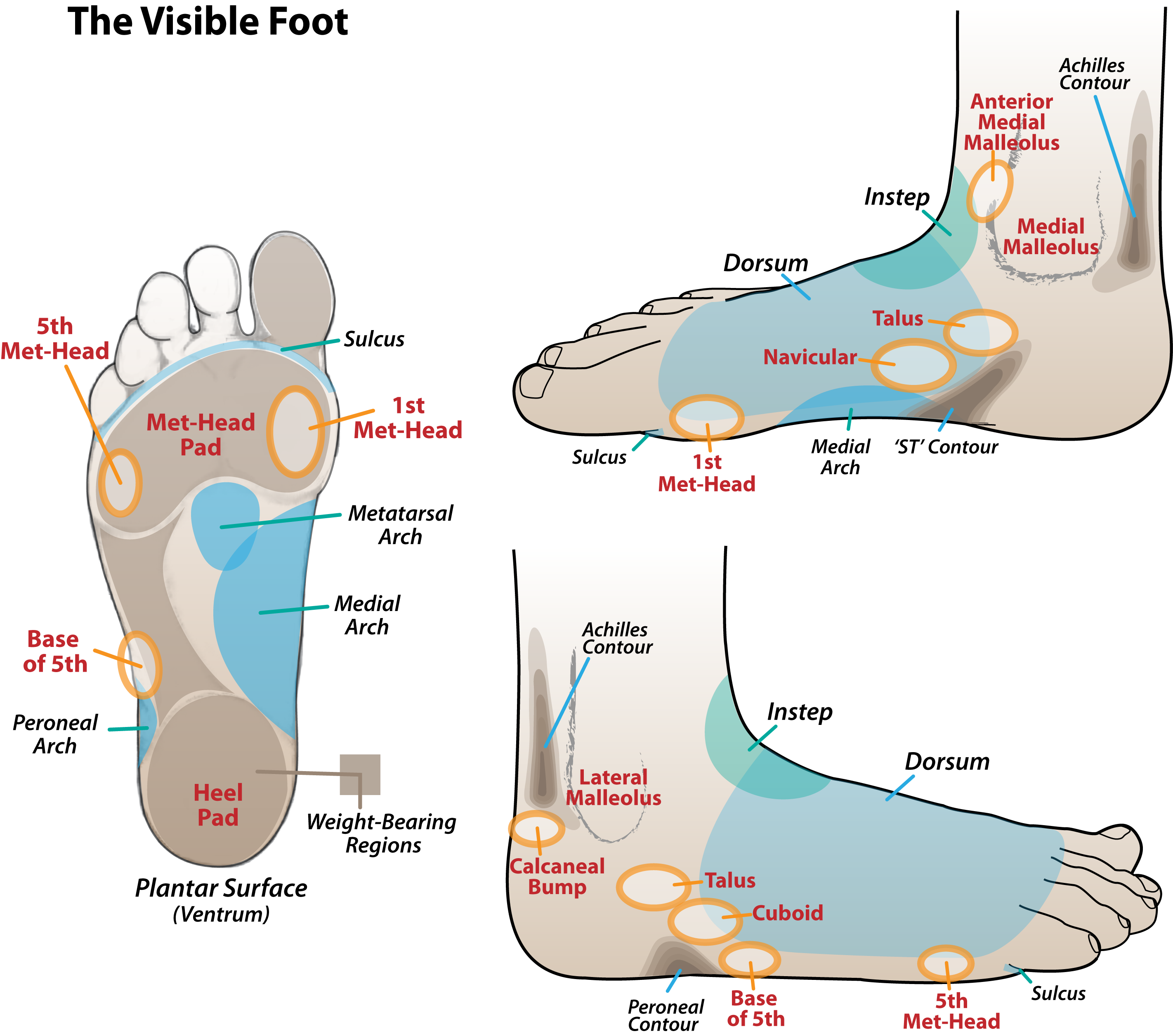
Cascade Dafo
Foot Definition The foot is a part of vertebrate anatomy which serves the purpose of supporting the animal's weight and allowing for locomotion on land. In humans, the foot is one of the most complex structures in the body.